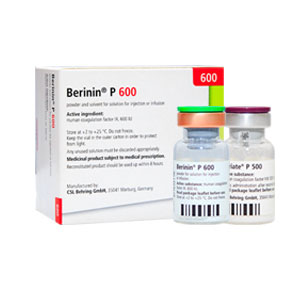
Coagulation factor 8
Extracted from Iranian plasma containing 500 international units concentrated Factor VIII per vial and produce under commercial name of “hemaketine” by biotest Company from Germany and “Berry Eight p” by CSL Behring company from Switzerland.
- Anti – coagulation factor
- Anti – hemophilia
- Anti – hemorrhage
- 250 injective units
- 500 injective units
- Effective compound: Coagulation factor VIII extracted from human plasma (500|U/vial)
- Excipients: glycine, sodium chloride, sodium citrate, calcium chloride, water for injections
- Prevention and treatment of bleeding in hemophilia A (factor 8 congenital deficiency)
- Prevention and treatment of bleeding in factor 8 Acquired deficiency
- Treatment of patients with Factor 8 inhibitors
In case of hypersensitivity to coagulation factor 8 or any of the excipients in the formulation
- Factor 8 solution must administrate through intravenous injection
- Dosage must determine individually based on bleeding causes, the surgery type, severity of factor VIII deficiency and bleeding amount.
- One proposed formulation for Approximate calculation of the required dose is:
- 0/5 × The favorable increase in factor8 (%)× body weight = the required amount
- As with any intravenous injective protein, there is hypersensitive allergic reaction possibility.
- There is possible that body start to produce anti-factor 8 anti-bodies (inhibitors) After continuous frequently treatments with factor 8
- because of possible infectious agents, there is a potential treat of infectious diseases transmission via human blood or plasma. Also, this probability exists about pathogens with unknown nature.
- It’s suggested that patients who receive plasma or blood drive products regularly, vaccinated against hepatitis B (BA).
- The Parvovirus B19 can be a treat for pregnant women (fetal infection) and patients with immunodeficiency or Polycythemia (Like Hemolytic anemia patients)
- Potential allergic reactions in some patients after factor VIII products administration include: Chills, rash and fever
- Headache, tingling, hypotension, severe fatigue, nausea, rapid pulse, feeling of pressure in the chest, irritation and vomiting rarely
- Frequent administration of factor VIII in high dosages can causes Intravascular hemolysis in B, A and AB blood groups due to presence of blood groups isoagglutinins
- Also, in some products high dosages of some products can causes hyperfibrinogenemia. Using other products with higher purity Reduces this risk.
- There is possible that patients with Type A hemophilia produce factor 8 inhibitors, risk potential is higher in first 20 t0 100 administration.
- Low – titer antibodies are mostly temporary and can be overcome with continued treatment with factor 8. But this is not high -titer high responding antibodies in bleeding episodes must control with by passing fraction of factor VIII inhibitors (activated Prothrombin complex concentrate) or activated factor VIIa.
- stored in 25°F
- protect it from light
- protect it from freezing
Molecule of factor 8 consists of two subunits (factor 8 and von willebrand factor) with different physiologic performances. Factor 8 is responsible for coagulation and act as an auxiliary factor with factor 9 in activating factor 10, then activated factor 10 convert Prothrombin to thrombin, thrombin converts fibrinogen into fibrin and clot is formed. In type A hemophilia patients factor 8 activity decrease significantly so alternative treatments are necessary.
Related Products
 https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/1.jpg
500
500
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-10 05:58:492016-08-01 05:12:59Anti-rabies human immunoglobulin
https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/1.jpg
500
500
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-10 05:58:492016-08-01 05:12:59Anti-rabies human immunoglobulin https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/1-300-dar-300.jpg
300
300
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-08 08:18:202016-08-01 05:20:35Coagulation factor 8
https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/1-300-dar-300.jpg
300
300
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-08 08:18:202016-08-01 05:20:35Coagulation factor 8 https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/2-300-dar-300.jpg
300
300
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-08 08:00:332016-07-13 08:50:33FH human albumin solution
https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/2-300-dar-300.jpg
300
300
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-08 08:00:332016-07-13 08:50:33FH human albumin solution https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/3-300-dar-300.jpg
300
300
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-08 07:48:552016-08-01 05:21:36Intravenous human immunoglobulin
https://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/02/3-300-dar-300.jpg
300
300
admin@ibrf.ir
http://ibrf.ir/en/ibrcont/uploads/2016/10/ibrf-en-logo-1.png
admin@ibrf.ir2016-02-08 07:48:552016-08-01 05:21:36Intravenous human immunoglobulin